
Tuple in Python: Complete Guide with Examples
When learning Python, one of the most important concepts to understand is data structures. Python provides several built-in data structures like lists, sets, dictionaries, and tuples. Among these, tuples play a key role in storing and organizing data. In this article, we will explore what a tuple is, why it is used, its advantages, and practical examples that make the concept easy to understand.

What is a Tuple in Python?
A tuple in Python is an ordered collection of elements. It is similar to a list, but unlike lists, tuples are immutable, meaning once you create a tuple, you cannot modify it.
In simple words:
- A list can be changed (add, remove, update items).
- A tuple cannot be changed once created.
This immutability makes tuples useful when you want to ensure that your data remains constant throughout the program.
How to Create a Tuple in Python
You can create a tuple by placing elements inside parentheses ( ) separated by commas.
Example 1: Creating a tuple
#Creating a tuple of fruits
fruits = (“apple”, “banana”, “cherry”)
print(fruits)
Output:
(‘apple’, ‘banana’, ‘cherry’)
Tuple with Different Data Types
Tuples can store elements of different data types, including strings, integers, floats, and even other tuples.
Example 2: Tuple with multiple data types
my_tuple = (10, “Hello”, 3.14, True)
print(my_tuple)
Output:
(10, ‘Hello’, 3.14, True)
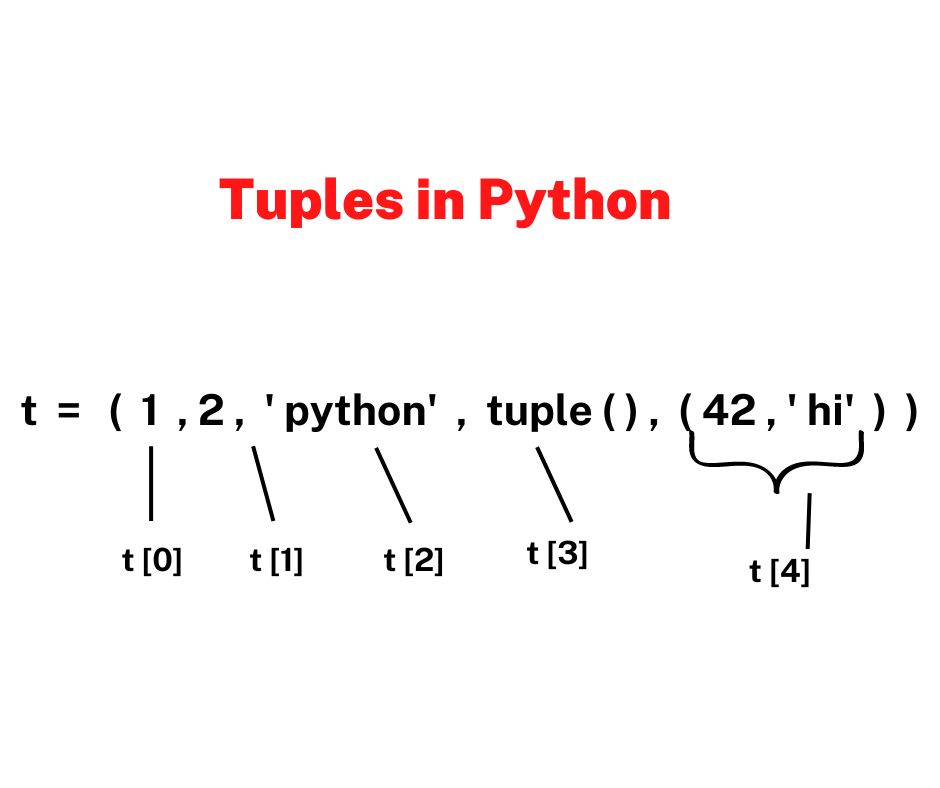
Accessing Tuple Elements
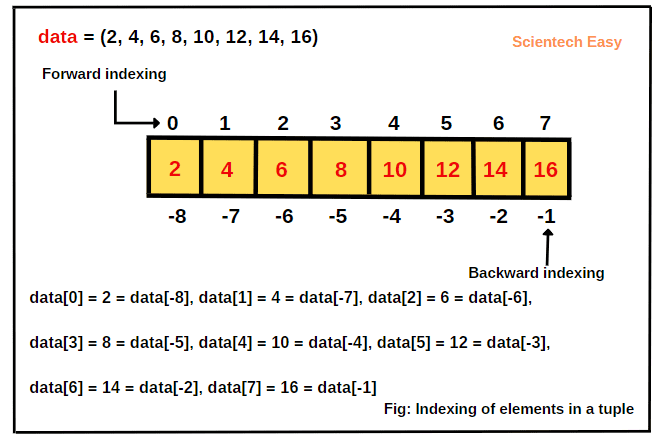
Since tuples are ordered, you can access elements using indexing. Indexing in Python starts from 0.
Example 3: Accessing elements by index
numbers = (5, 10, 15, 20)
print(numbers[0]) # First element
print(numbers[2]) # Third element
Output:
5
15
You can also use negative indexing to access elements from the end.
print(numbers[-1]) # Last element
20
Tuple Slicing
Just like lists, tuples support slicing.
Example 4: Slicing a tuple
colors = (“red”, “green”, “blue”, “yellow”, “purple”)
print(colors[1:4]) # Elements from index 1 to 3
Output:
(‘green’, ‘blue’, ‘yellow’)
Why Use Tuples Instead of Lists?
- Immutability: Tuples are fixed, so they are safer for storing constant data.
- Performance: Tuples are faster than lists in terms of execution speed.
- Hashable: Tuples can be used as keys in dictionaries, while lists cannot.
Tuple Methods
Even though tuples are immutable, Python provides some built-in methods for working with them.
Example 5: Using tuple methods
animals = (“cat”, “dog”, “cat”, “rabbit”)
#Count occurrences of an element
print(animals.count(“cat”))
#Find the index of an element
print(animals.index(“dog”))
Output:
2
1
Nested Tuples
A tuple can also contain other tuples inside it, known as nested tuples.
Example 6: Nested tuple
nested = ((“a”, “b”), (1, 2, 3))
print(nested[0]) # First inner tuple
print(nested[1][2]) # Access element inside nested tuple
Output:
(‘a’, ‘b’)
3
Tuple Unpacking
You can assign tuple elements to multiple variables at once. This is called tuple unpacking.
Example 7: Tuple unpacking
person = (“John”, 25, “Engineer”)
name, age, profession = person
print(name)
print(age)
print(profession)
Output:
John
25
Engineer
When to Use Tuples in Python?
- Use lists when data is expected to change frequently.
- Use tuples when data must remain constant.
Examples in real life:
- Storing fixed coordinates (latitude, longitude).
- Keeping constant configurations.
- Returning multiple values from a function.
Key Differences Between List and Tuple
| Feature | List | Tuple |
|---|---|---|
| Syntax | [ ] | ( ) |
| Mutable | Yes | No |
| Performance | Slower | Faster |
| Dictionary Key | Not allowed | Allowed |
Highlights
Tuples in Python are a powerful and efficient data structure. They are ordered, immutable, and capable of storing multiple data types. By using tuples, you can make your programs safer and faster when dealing with fixed data. Whether you are working with constant values, returning multiple outputs, or storing coordinates, tuples are an excellent choice.
Understanding tuples not only strengthens your Python basics but also helps you write clean, reliable, and optimized code.
For the Latest Jobs Notifications: Click Here
Join With Us On WhatsApp: Click Here
Join With Us On LinkedIn: Click Here
Free Python Learning: Click Here
DISCLAIMER
The Recruitment Information Provided above is for Informational Purposes only. The above Information has been taken from the official site of the Organization. We do not provide any Recruitment guarantee. Recruitment is to be conducted in accordance with the company’s official recruitment process. We don’t charge any fee for providing this job Information.