Understanding Arithmetic Operators in Python
ARITHEMATIC OPERATOR
Python provides a set of arithmetic operators that allow you to perform mathematical computations efficiently. These operators work with both integers (int) and floating-point numbers (float). Let’s explore each of them with examples.
Arithematic operators-Signs

Explore Arithmetic Operators in Python
| Situations | Operator | Description | Syntax with example |
| 1 | + | Adding two operands | a+b (3+2=5) |
| 2 | – | Subtract two operands | a-b (3-2=1) |
| 3 | * | Multiply two operands | a*b (3*2=6) |
| 4 | / | Divide the operands | a/b (3/2=1.5) |
| 5 | // | Use to remove decimal | a//b (3/2=1) |
| 6 | ** | Square Root | a**b (3**2=9) |
| 7 | % | Find out reminder value | a%b (3%2=1) |
Python: A Comprehensive Guide for Beginners
1. Addition (+)
The + operator adds two numbers together.
Example:

This is the perfect example of addition which is coding in python.
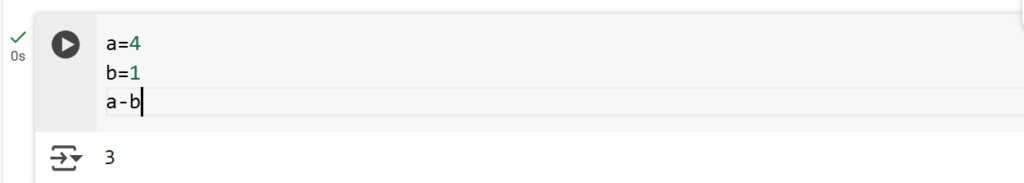
2. Subtraction (-)
The - operator subtracts one number from another.
Example:
3. Multiplication (*)
The * operator multiplies two values.
Example:

4. Division (/)
The / operator performs division and always returns a float.
Example:

5. Floor Division (//)
The // operator performs division but rounds down the result to the nearest whole number.
Example:

6. Modulus (%)
The % operator gives the remainder left after dividing one number by another.
Example:

7. Exponentiation (**)
The ** operator is used to exponentiate a number, raising it to a specified power.
Example:

Conclusion
Arithmetic operators are the foundation of mathematical computations in Python. Whether you need to perform basic calculations or complex mathematical operations, these operators provide a straightforward approach to handling numerical data.
Ready jobs for after learning the python